LLC vs C-Corp. Which Should I Choose?
Considering the Right Legal Structure for Your Startup?
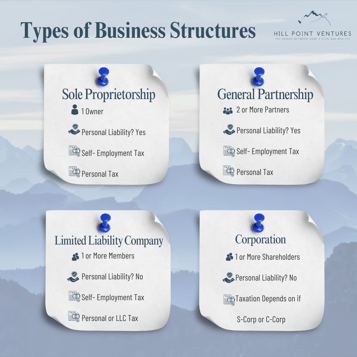
As startups and entrepreneurs, choosing the appropriate legal structure is pivotal for long-term success. Today, let's explore the two most common business structures: LLC vs. C-Corp. Here's a breakdown of the pros and cons:
Limited Liability Company (LLC):
Pros:
1️⃣ Flexibility: LLCs offer a flexible management structure and fewer formalities compared to C-Corps. Quick example: a c-corp has a board of directors, board meetings, shareholder meeting, resolutions, and minutes of those meetings to make and document major decisions. LLCs offer a much more informal and flexible structure.
2️⃣ Pass-through Taxation: Profits and losses can pass through to the owners' personal tax returns, potentially resulting in lower taxes. Corporations, on the other hand, are taxes as a business and then dividends paid to shareholders are taxed as income.
3️⃣ Limited Liability: Members are protected from personal liability for the company's debts and obligations. The only assets at risk are the LLCs.
Cons:
1️⃣ Capital Raising Challenges: LLCs face limitations in raising capital through equity financing. LLCs are in essence, a partnership with shareholder liability protection. Any way you slice it, you are talking about percentages, not shares.
2️⃣ Informality: While less formalities can be advantageous, lack of structure might lead to governance issues and disputes among members. You are much more dependent on the judgment and discretion of the members than you are with a board of directors.
3️⃣ Limited Lifespan: In some jurisdictions, LLCs have a limited lifespan, which may not be ideal for long-term business planning.
Corporation (C-Corp):
Pros:
1️⃣ Access to Capital: C-Corps have greater access to capital through the issuance of stock, making them attractive to investors. LLCs are an evolution of the partnership, and therefore are more complicated structures for selling equity.
2️⃣ Classes of Stock: Corporations can issue different kinds of stock that come with different privileges, most often with common stock, which has voting rights, and preferred stock, which does not but has priority over common stock when getting paid.
3️⃣ Corporate Formalities: While more rigorous, following corporate formalities can offer clarity in decision-making and protect the corporate veil. It also de-risks an investment by ensuring a strong decision making process is in place.
Cons:
1️⃣ Double Taxation: C-Corps are subject to double taxation – once at the corporate level and again on dividends distributed to shareholders.
2️⃣ Complexity and Compliance: Maintaining a C-Corp requires adherence to various regulatory and compliance requirements, potentially increasing administrative burdens and costs.
3️⃣ Ownership Restrictions: Unlike LLCs, which can have a flexible ownership structure, C-Corps often have more stringent ownership rules.
When it comes to raising capital:
-LLCs: Suitable for businesses seeking simplicity and flexibility but may face challenges in attracting external investment.
-C-Corps: Ideal for ventures aiming for rapid growth and significant funding, but require a higher level of formality and compliance.
The choice between LLC and C-Corp depends on your specific business goals, long-term strategy, and appetite for complexity. Remember to consult with legal and financial advisors to make an informed decision tailored to your unique circumstances.

 By
By


